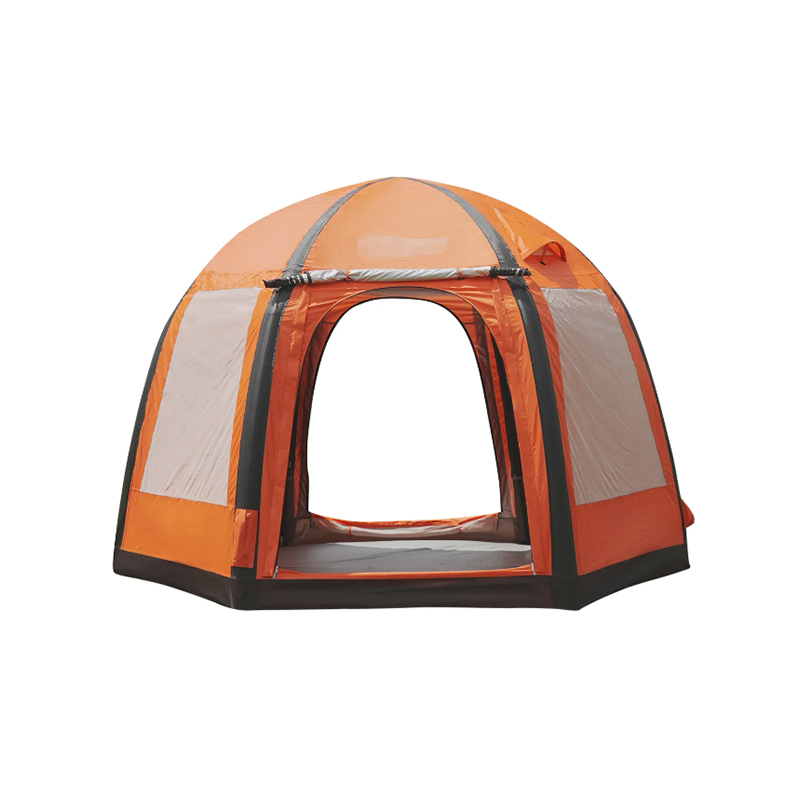
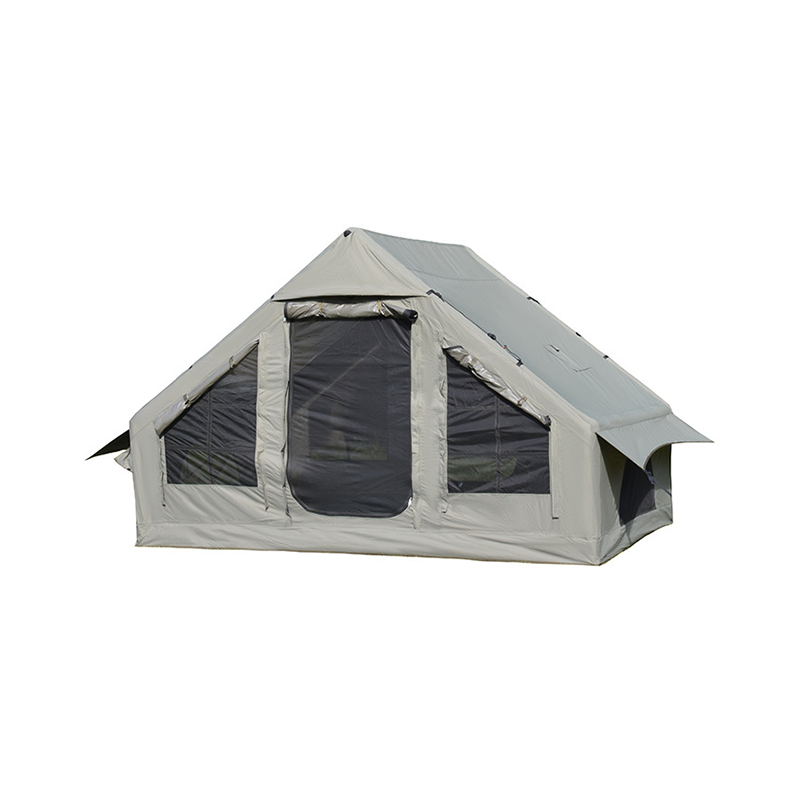
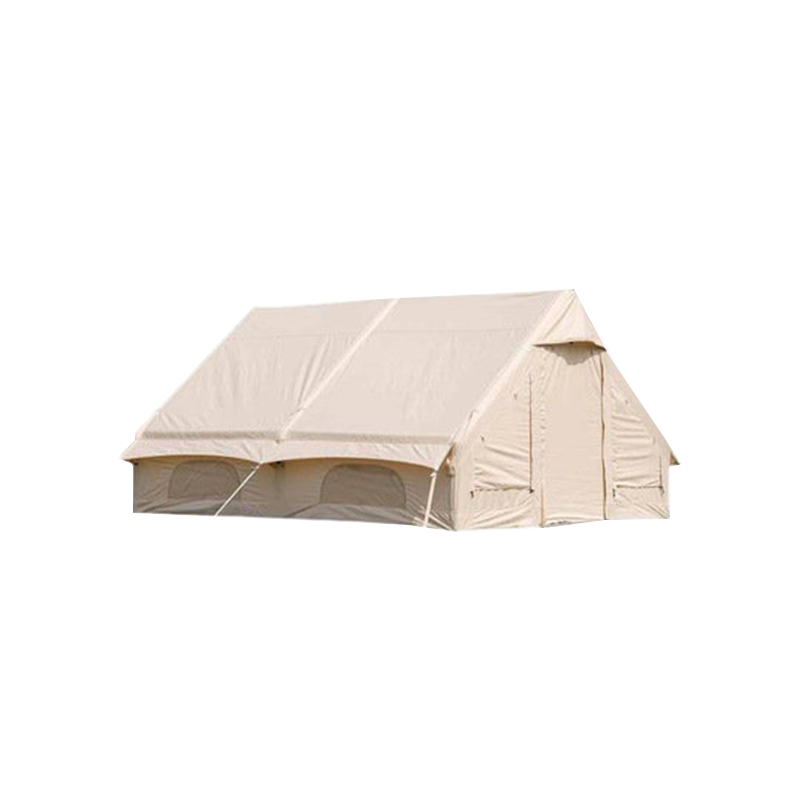
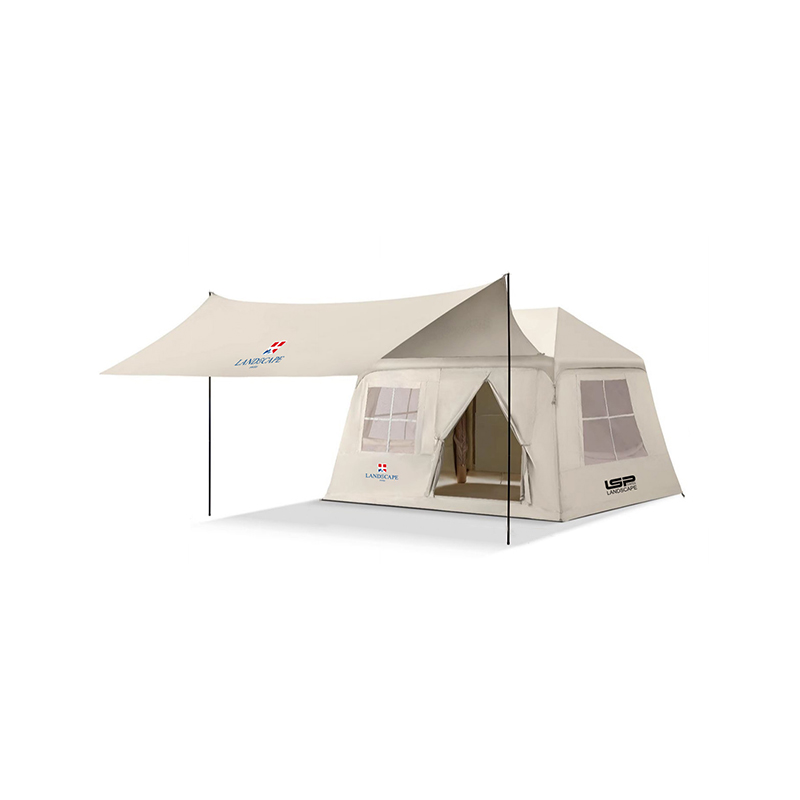
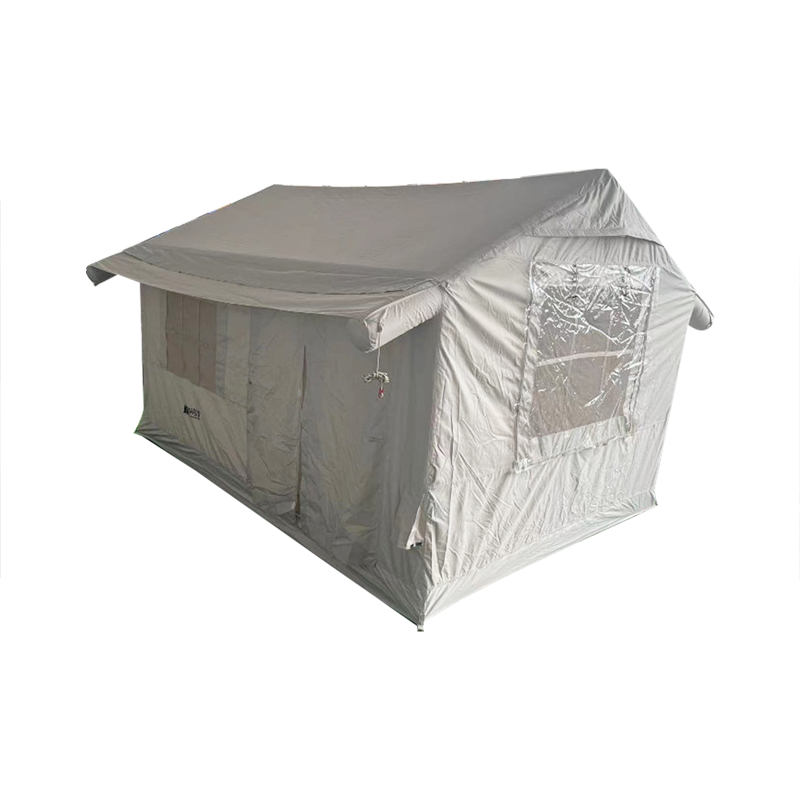
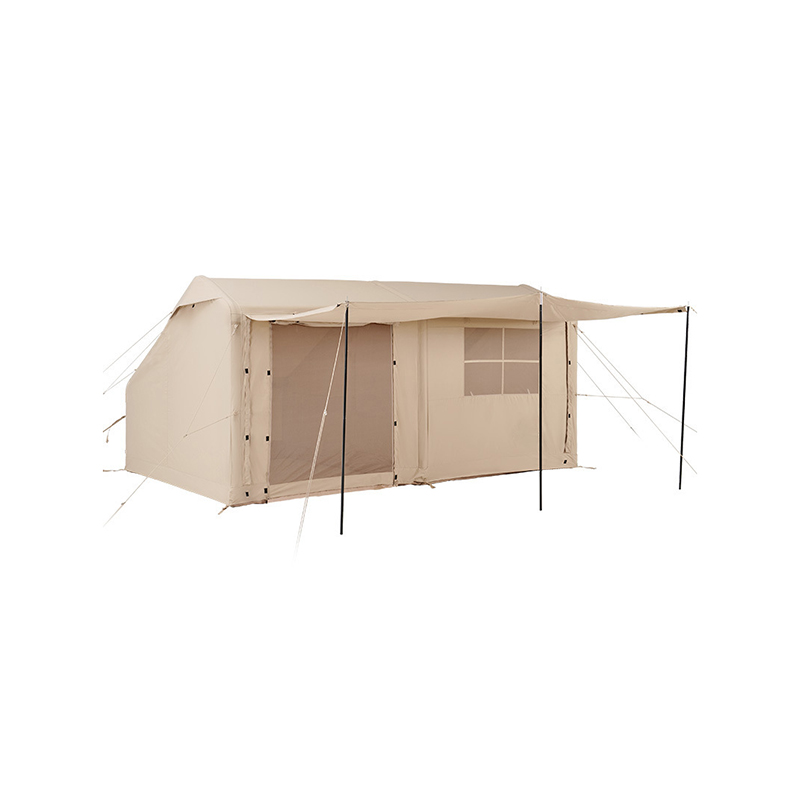
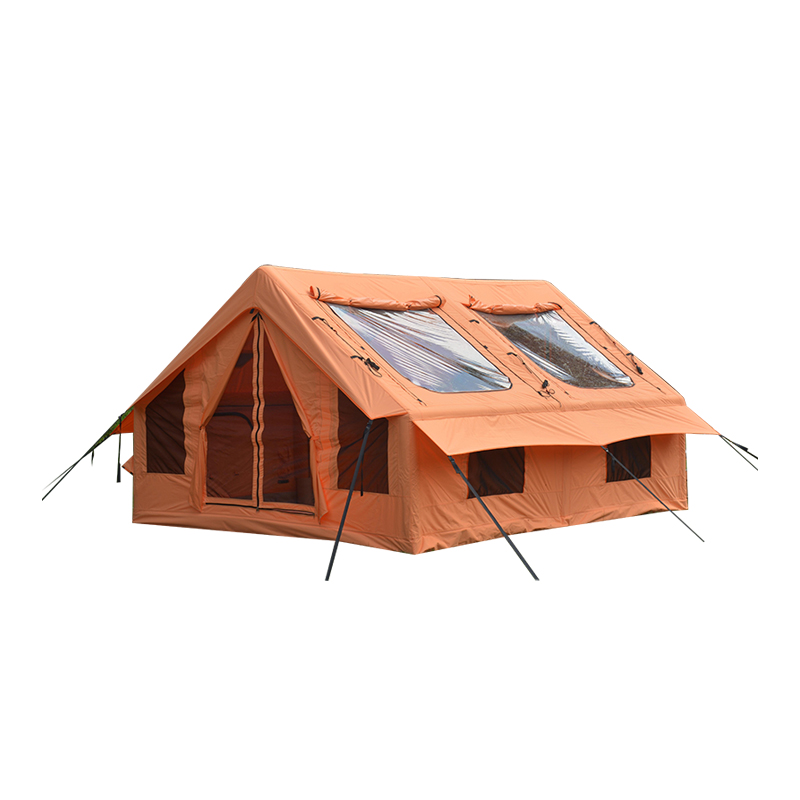
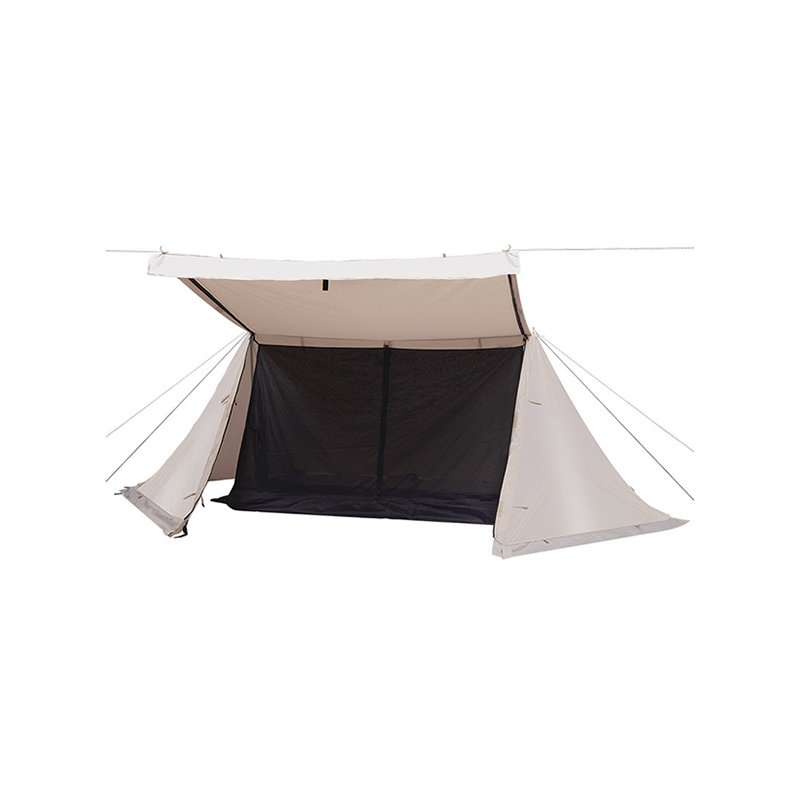
Angled and Curved Canopy Design for Efficient Water Runoff
The design of the canopy in an Inflatable Tent With Canopy is crucial for preventing water accumulation. Modern tents incorporate engineered slopes, curves, and peaked sections that allow rainwater to naturally flow toward the edges of the structure. These angles are not arbitrary—they are calculated based on canopy size, beam placement, and material stretch characteristics to balance water shedding with interior usable space. In larger tents, multiple peaks or ridge lines may be implemented, creating channels that guide water along predetermined paths while preventing sagging at midpoints. The curvature also reduces localized stress on the inflatable beams, ensuring structural integrity during heavy rainfall. By facilitating continuous runoff, the angled canopy reduces the risk of water pooling, which can compromise both user safety and the longevity of the tent.
Reinforced Drainage Channels and Seam-Integrated Gutters
Some high-performance Inflatable Tent With Canopy models incorporate reinforced drainage channels or integrated gutter-like features along the seams and ridges. These channels collect and direct rainwater away from critical areas, such as the junctions of inflatable beams and fabric panels. The channels are often constructed with additional waterproof fabric layers or coated materials, ensuring durability under sustained rainfall. By combining structural reinforcement with water guidance, these systems reduce the risk of seam stress and localized sagging. In commercial or event tents, the drainage channels are designed to evenly distribute water load along the canopy surface, preventing deformation of the inflatable beams. This integration of structural support and drainage enhances overall stability and longevity, even in demanding weather conditions.
Hydrophobic and Waterproof Canopy Materials
The canopy fabric of the Inflatable Tent With Canopy typically employs high-strength polyester or PVC-coated textiles treated with hydrophobic coatings such as polyurethane or silicone. These coatings significantly reduce water adhesion to the surface, allowing rain to bead and flow off rapidly. This treatment not only prevents pooling but also protects the canopy from long-term degradation caused by moisture penetration, mold, or mildew. Additionally, the coatings improve UV resistance and maintain fabric tensile strength, ensuring that water-shedding performance remains consistent over multiple uses. By combining material engineering with design angles and structural tension, the tent can efficiently manage water flow, minimizing weight loads on the inflatable beams and preserving interior dryness.
Tensioned Inflatable Beam Structure
The inflatable beams of the tent play a dual role in providing structural support and enabling effective drainage. When fully inflated, these beams maintain a tensioned canopy surface that prevents sagging or low points where water could accumulate. Some designs feature variable inflation zones, which create slightly higher central areas or distributed peaks to facilitate runoff. The tension ensures that water naturally moves toward the edges, rather than pooling in midsections, and the inflatable nature of the beams allows for slight flexing without compromising shape or integrity. This tensioned system is particularly important for large-scale tents or those used in outdoor events, where heavy rain could otherwise compromise stability, safety, and interior usability.
Edge and Perimeter Water-Shedding Features
Effective water management extends beyond the canopy itself. Many Inflatable Tent With Canopy models feature extended eaves, overhangs, or peripheral gutters designed to direct runoff away from entrance areas and high-traffic zones. These edge features can include reinforced fabric layers, integrated channels, or subtle slopes that control where water drips onto the ground. Properly managed runoff prevents erosion around the tent’s anchor points and protects users from splashing or puddles near entrances. Some designs include optional stakes, ropes, or weighted anchors that maintain canopy position and ensure that perimeter water-shedding remains effective during windy conditions, enhancing both safety and comfort.
Maintenance, Inflation, and User Guidelines for Optimal Drainage
Even with engineered water-shedding features, proper use is critical to prevent pooling. Users must maintain correct inflation pressure to keep canopy surfaces taut, preventing sagging midpoints where water could accumulate. Regular inspection of seams, drainage channels, and peripheral features ensures that debris or minor fabric wear does not impede water flow. Placement on even terrain prevents water from collecting on one side, which could stress inflatable beams unevenly. Some models include visual indicators or ports to monitor canopy tension and beam integrity, allowing timely adjustments during prolonged rainfall. By combining proper setup, regular maintenance, and environmental awareness, users can maximize drainage efficiency, preserve tent structure, and maintain a safe, dry interior.



 English
English 中文简体
中文简体