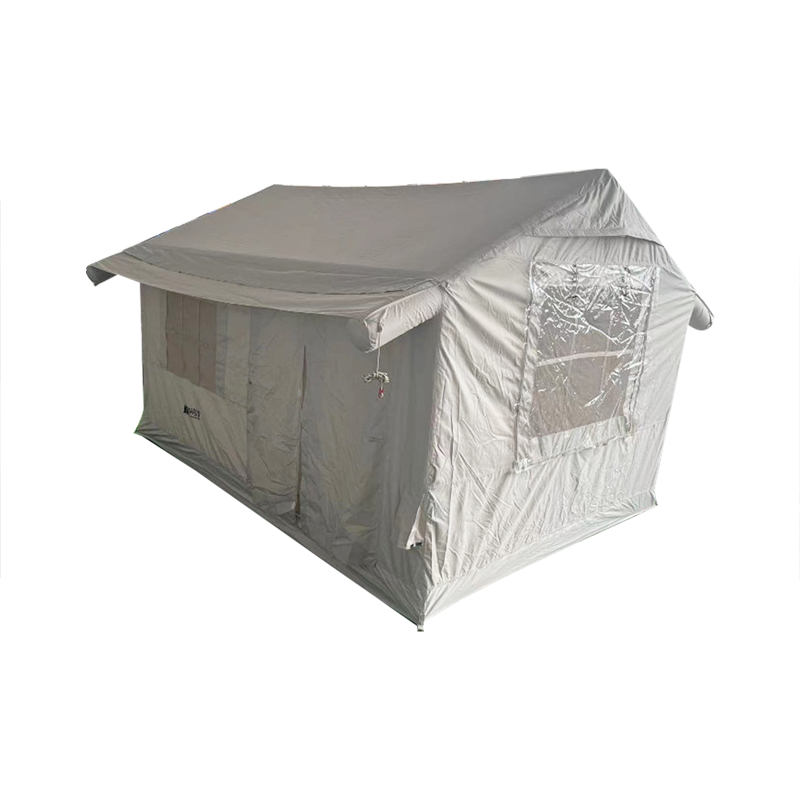
The See-Through Hunting Blind relies heavily on a durable, heavy-duty frame to ensure long-term stability, especially in challenging weather conditions. Frames are typically made from materials like steel, aluminum, or fiberglass, which are chosen for their combination of strength, lightweight properties, and resistance to corrosion. The robust frame serves as the foundational structure that holds the blind's fabric taut and prevents sagging or warping over time. By distributing stress evenly across the structure, the frame helps maintain the blind’s integrity during high winds. In some models, the frame may feature additional reinforced corners, cross-bracing, and stabilizing bars to handle significant wind loads without bending, ensuring that the blind maintains its shape and functionality in harsh conditions.
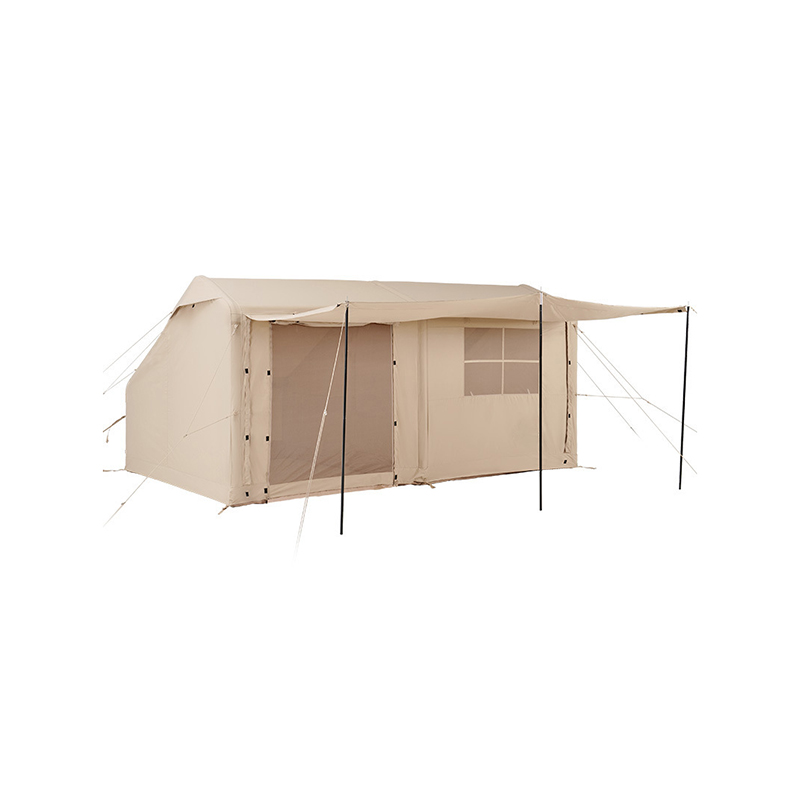
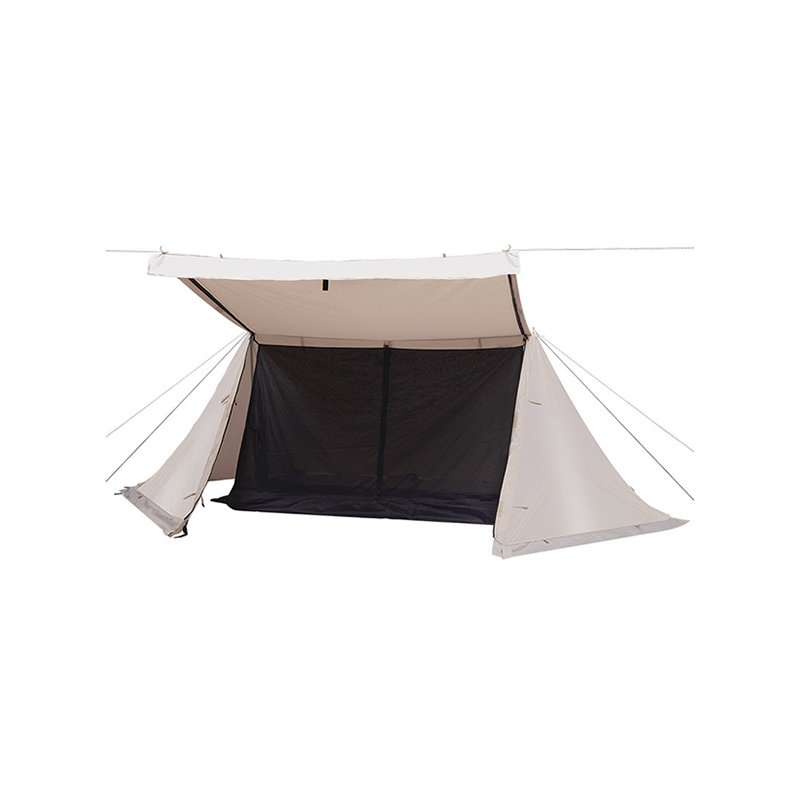
Anchoring is critical for See-Through Hunting Blinds to stay in place during gusty winds, especially in open environments with little natural cover. Many hunting blinds are equipped with built-in anchor points and tie-down straps that can be used to secure the blind to nearby trees, posts, or other solid structures. Some models come with ground stakes that allow hunters to drive the blind firmly into the earth. For areas with no trees, sandbag pouches or stakes that can be filled with dirt or rocks add additional ballast at the base of the blind. This anchor system minimizes movement, reduces the likelihood of the blind shifting, and provides additional stability to prevent the blind from toppling over, even during sustained winds.
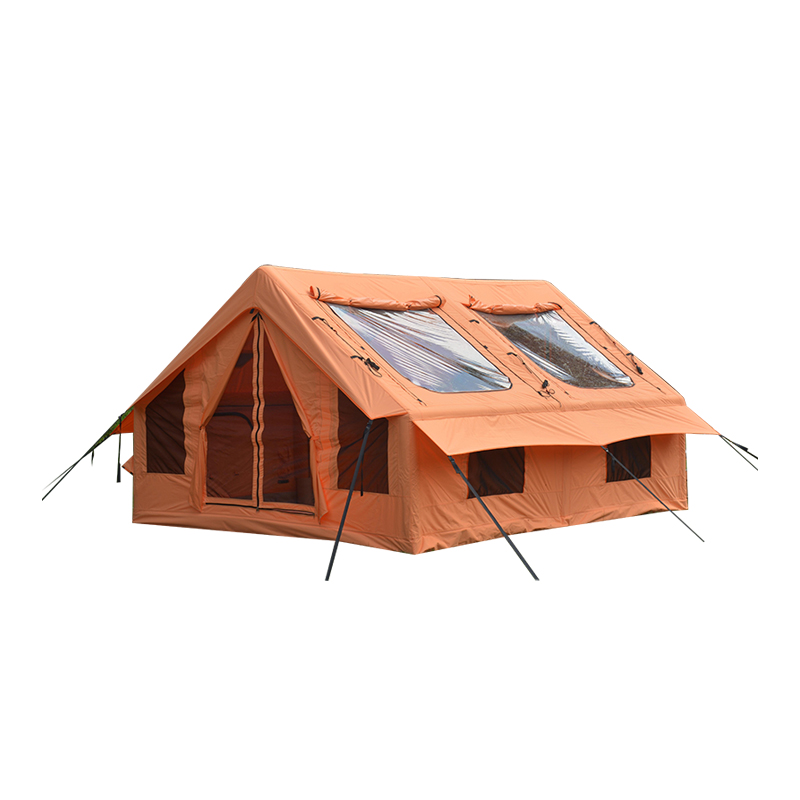
The See-Through Hunting Blind is designed with aerodynamic principles in mind to reduce wind resistance. Many models feature sloped or tapered profiles that allow wind to pass over the structure more smoothly rather than creating drag. The materials used for the outer shell are typically wind-resistant fabrics such as polyester blends or ripstop nylon, which are designed to resist billowing and flapping in high winds. Some models also feature ventilation slits or windbreaks built into the design, allowing air to flow through without pushing on the blind. These aerodynamic and weather-resistant designs help ensure that the blind remains stable and functional even in gusty conditions, reducing the chances of wind damage or structural collapse.
The weight distribution of the See-Through Hunting Blind is a key factor in its stability. Many models have a lower center of gravity where heavier components are placed toward the bottom of the blind, typically through reinforced base materials or weighted fabrics. This helps anchor the blind to the ground and reduces the likelihood of it tipping over in high winds. The added weight in the lower portion prevents wind from lifting the blind at its corners or edges, while also preventing excessive shifting. This design ensures that the blind remains grounded, even in areas where natural cover may be sparse and wind speeds are high. Some models also feature reinforced bottoms or integrated weight systems, such as ballast pockets, to further enhance stability.
To provide additional stability, See-Through Hunting Blinds often come with ground stakes or stabilizing pegs that help secure the structure to the ground. These pegs are typically made from steel or heavy-duty plastic and are designed to be driven into the ground, providing extra anchorage. The stakes are usually placed at strategic points along the blind’s edges and corners, where wind pressure is most likely to be exerted. Some models include quick-install stakes, allowing for fast and secure setup, even in uneven terrain. These stabilizing features can be especially beneficial in open areas where natural barriers like trees, rocks, or shrubs are absent, ensuring that the blind remains in place without shifting or toppling.
The corners and edges of a See-Through Hunting Blind are critical points that experience the highest stress, especially in windy conditions. To address this, many hunting blinds incorporate reinforced corner stitching, double-layered edges, or steel reinforcements at key stress points. These reinforcements ensure that the blind maintains its structural integrity under pressure, preventing the material from ripping or sagging. Some designs even feature tightened corner brackets or cross-braced supports at the bottom corners to further reduce the risk of tearing or damage. This attention to detail at the edges makes the blind significantly more resilient and less prone to wear and tear over time.



 English
English 中文简体
中文简体